EP4 receptor antagonist 1
CAS No. 2287259-07-6
EP4 receptor antagonist 1( —— )
Catalog No. M26201 CAS No. 2287259-07-6
EP4 receptor antagonist 1 inhibits human and mouse EP4 receptor with IC50s of 6.1 nM and 16.2 nM, respectively.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 284 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 527 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameEP4 receptor antagonist 1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionEP4 receptor antagonist 1 inhibits human and mouse EP4 receptor with IC50s of 6.1 nM and 16.2 nM, respectively.
-
DescriptionEP4 receptor antagonist 1 inhibits human and mouse EP4 receptor with IC50s of 6.1 nM and 16.2 nM, respectively. IC50s >10 μM for human EP1, EP2,and EP3 receptors.EP4 receptor antagonist 1 is a highly potent and selective competitive prostanoid EP4 receptor antagonist for cancer immunotherapy.(In Vitro):EP4 receptor antagonist 1 inhibits the activity of the CRE reporter in HEK293 cells with an IC50 of 5.2±0.4 nM in a dose-dependent manner. EP4 receptor antagonist 1 dose-dependently inhibits PGE2-stimulated β-arrestin recruitment in HEK293-EP4 cells with an IC50 of 0.4±0.1 nM. EP4 receptor antagonist 1 inhibits PGE2-stimulated cAMP accumulation in HEK293-EP4 cells with an IC50 of 18.7±0.6 nM in a dose-dependent manner. EP4 receptor antagonist 1 (1 nM-10 μM) reverses PGE2-induced ERK phosphorylation in a concentration-dependent manner. The IC50s are >10 μM for human EP1, EP2, and EP3 receptors.(In Vivo):EP4 receptor antagonist 1 (1 mg/kg; i.v.) demonstrates moderate clearance of 1.7 L/h/kg in mice with a corresponding favorable half-life of 4.1 h. EP4 receptor antagonist 1 (5 mg/kg; orally) exhibits good bioavailability of 48.0% in mice with a corresponding favorable half-life of 4.7 h. EP4 receptor antagonist 1 (16, 50, and 150 mg/kg; oral) causes significant inhibition of tumor growth in BALB/c female mice. No significant body weight loss is found in any mouse cohorts. EP4 receptor antagonist 1 is well tolerated in mice at the tested dosage.
-
In VitroThe antagonistic effect of EP4 receptor antagonist 1 (Compounds 59) on human EP4 in calcium flux assay with an IC50 of 6.1±0.2 nM in CHO-Gα16 cells overexpressing human EP4 receptor. The antagonistic effect of EP4 receptor antagonist 1 on human EP4 in calcium flux assay with an IC50 of 16.2±1.7 nM in CHO-Gα16 cells overexpressing mouse EP4 receptor.EP4 receptor antagonist 1 dose dependently inhibits PGE2-stimulated cAMP accumulation in HEK293-EP4 cells with an IC50 of 18.7±0.6 nM. EP4 receptor antagonist 1 dose-dependently inhibits the activity of the CRE reporter in HEK293 cells with an IC50 of 5.2±0.4 nM.EP4 receptor antagonist 1 dose-dependently inhibits PGE2-stimulated β-arrestin recruitment in HEK293-EP4 cells with an IC50 of 0.4±0.1 nM.EP4 receptor antagonist 1 (1 nM-10 μM) reverses PGE2-induced ERK phosphorylation in a concentration-dependent manner. Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:CHO-EP4 cells Concentration:1 nM, 100 nM, 10 μM Incubation Time:Pretreated for 20 min and then subjected to 30 nM PGE2 simulation for 10 min.Result:Reversed PGE2-induced ERK phosphorylation in a concentration-dependent manner.
-
In VivoEP4 receptor antagonist 1 (16, 50, and 150 mg/kg; orally; once daily for two weeks) causes significant inhibition of tumor growth in BALB/c female mice. No significant body weight loss is found in any mouse cohorts. EP4 receptor antagonist 1is well tolerated in mice at the tested dosage.EP4 receptor antagonist 1 (1 mg/kg; intravenously) demonstrates moderate clearance (CL=1.7 L/h/kg) in mice with a corresponding favorable half-life (t1/2) of 4.1 h.EP4 receptor antagonist 1 (5 mg/kg; orally) exhibits good bioavailability (F=48.0%) in mice with a corresponding favorable half-life (t1/2) of4.7 h. Animal Model:BALB/c female mice (6-week-old)bearing CT26 colon cancer model Dosage:16, 50, and 150 mg/kg Administration:Orally; once daily for two weeks Result:Tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was 24.6% at 16 mg/ kg, 54.7% at 50 mg/kg, and 63.8% at 150 mg/kg. Animal Model:BALB/c female mice Dosage:1 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg (Pharmacokinetic Analysis) Administration:Intravenously or orally at a dose of 1 mg/kg (5 mL/kg) and 5 mg/kg (10 mL/kg),respectively.Result:Demonstrated moderate clearance ( CL=1.7 L/h/kg) in mice with a corresponding favorable half-life (t1/2) of4.1 h at a dose of 1 mg/kg (intravenously). Exhibited good bioavailability (F=48.0%) in mice with a corresponding favorable half-life (t1/2) of4.7 h at a dose of 5 mg/kg (orally).
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetProstaglandin Receptor
-
RecptorHIV-1| IFN-γ| IKK| IL Receptor| JAK| NADPH-oxidase| NF-κB| NO| ROS| STAT| TLR| TNF-α
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2287259-07-6
-
Formula Weight458.441
-
Molecular FormulaC23H21F3N4O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (218.14 mM)
-
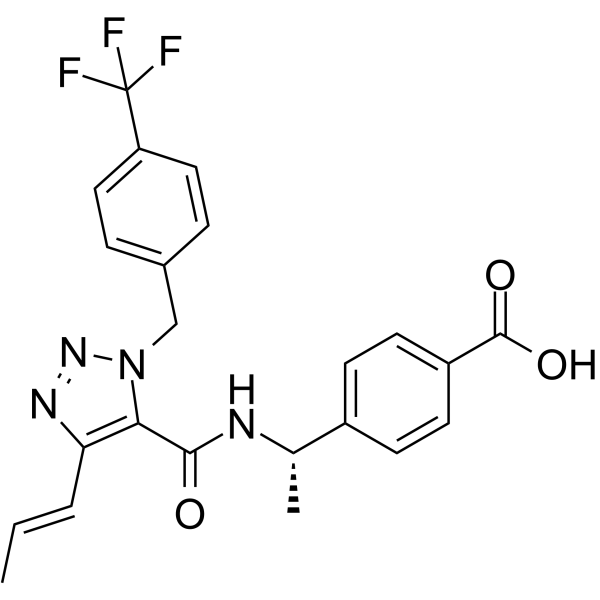
SMILESC\C=C\c1nnn(Cc2ccc(cc2)C(F)(F)F)c1C(=O)N[C@@H](C)c1ccc(cc1)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Antimicrobial activity and synergy of antibiotics with two biphenyl compounds, protosappanins A and B from Sappan Lignum against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;67(10):1439-47.
molnova catalog



related products
-
CR6086
CR6086 (CR-6086) is a potent, selective prostaglandin E2 receptor 4 (EP4) antagonist with Ki of 16.6 nM (hEP4 receptor).
-
Secoxyloganin
Secoxyloganin possesses a hepato-protective effect. Secoxyloganin possesses antibacterial activity.
-
L-798106
L-798106 (CM9) is a selective and potent prostaglandin-like EP3 receptor antagonist that inhibits EP4, EP1, and EP2 receptors, suppresses levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in atherosclerosis, and attenuates PGE2-induced cough.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


